$1.7 Trillion Spending Package Passed By Senate – What Made The Cut?
An overwhelming $1.7 trillion spending package was passed by a senate on Thursday, which includes record amounts for domestic programs and defense priorities as lawmakers were confused to approve the sweeping bill as a foreboding winter storm has threatened to paralyze the capital of the nation.
Moreover, The House was poised to the suit later Thursday and approve the measure to fund the remaining of the 2023 fiscal year that runs through September 30 and avoid a partial government shutdown which will take effect on Saturday, 12:01 AM.
According to a published post by USA Today, the Senate’s 68-29 vote came the day after the president of Ukraine, Volodymyr Zelenskyy alleged a joint session of Congress and made lawmakers approve billions in additional military, economic and humanitarian assistance in an attempt to repel Russia’s invasion. The bill spent includes roughly $45 billion for Ukraine.
Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer, D-N.Y., said on the floor before the vote that This is one of the most significant appropriations packages they have done in a very long time and The range of people it helps is large. After a lot of struggles and compromise, the Senate is assisting the government with aggressive investment in American families, workers, and national defense.
The bipartisan legislation would distribute $772.5 billion for non-defense discretionary programs and $858 billion in defense funding. Aside from additional emergency assistance to Ukraine, the delivered package includes money for NATO allies as well as funding for rural development, food assistance programs, and help for the military and veterans.
Despite running 4,000 pages or more, the measure excluded several measures demanded by progressive advocates, which include the extension of a more generous child tax credit and legislation known as the EQUAL Act that would remove federal sentencing disparities between drug offenses involving crack cocaine and powder cocaine. Despite being excluded from the package, several agencies and programs are still going to receive a boost in spending.
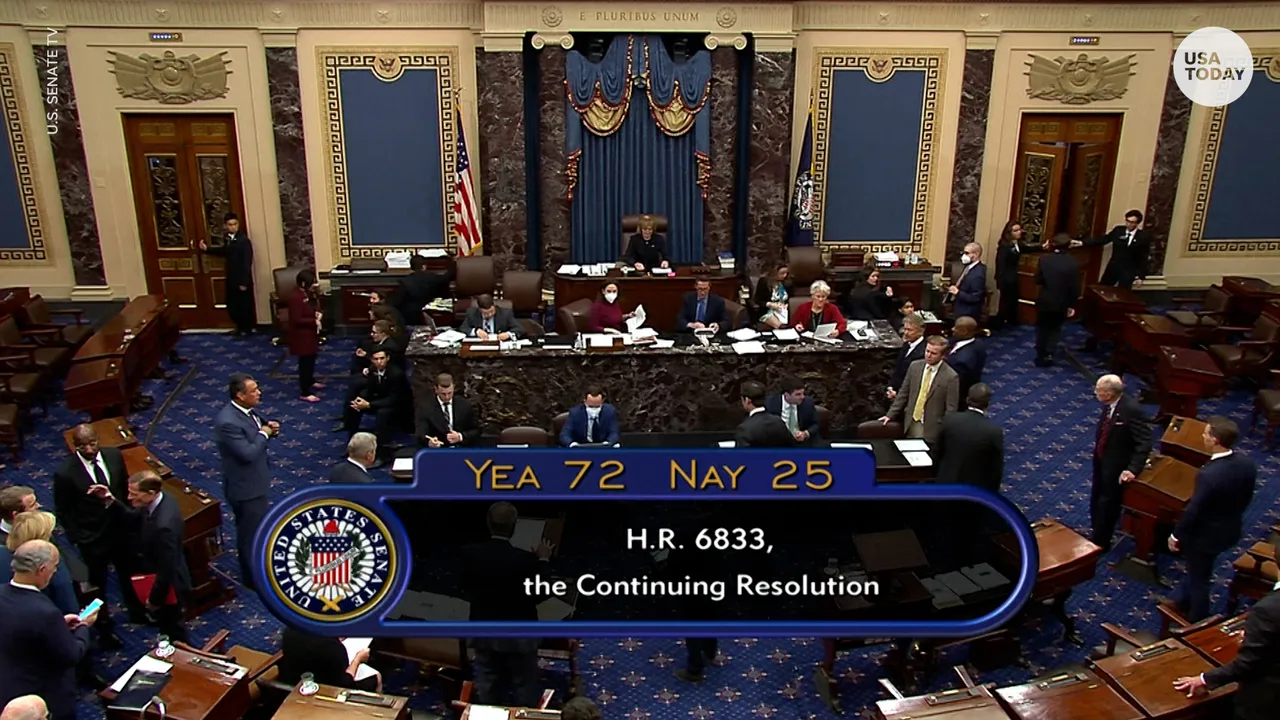
The Senate overwhelmingly passed a $1.7 trillion spending package Thursday that includes record amounts for domestic programs and defense priorities as lawmakers scrambled to approve the sweeping bill as a foreboding winter storm threatened to paralyze the nation’s capital. (Photo: USA Today)
Ukrainian Aid and a TikTok ban: what drove the cut?
• TikTok ban: The spending bill needs the Biden administration to establish guidelines to erase TikTok from government devices over concern about the social media platform’s Chinese parent company ByteDance.
• Electoral Count Act: Legislation to reshape the 1887 Electoral Count Act, which was at the center of Donald Trump’s attempt to overturn the 2020 election results, was among the pieces of legislation included in the sweeping spending bill. The bill was an effort to prevent a repetition of the chaos engulfing the Jan. 6 certification of the Electoral College tabulation.
• Ukrainian aid: according to Sen. Patrick Leahy, the Democratic chairman of the Senate Appropriations Committee, The U.S. has already provided $68 billion in military, economic and humanitarian aid to Ukraine since the invasion of Russia.
• defense spending increased: Defense spending will increase by nearly 10% including a pay raise for troops rise in housing and food allowances for military families and increased funding for public school constructions on military bases. The bill also distributed more than $106.2 million to repair military facilities that hurricanes Ian and Fiona damaged.
• Workplace protections: The Senate also included
• Measures that would add protections for pregnant workers, including the Pregnant Workers Fairness Act, which needs employers to provide basic accommodation for pregnant employees.
What Was Left Out Of The Larger Child Tax Credit Nixed?
• Child tax credit: even though it is a top priority for Democrats, a child tax credit expansion that started in response to the pandemic was excluded from the sweeping bill. Democratic lawmakers were looking to revive the temporary expansion of the program featured in the American Rescue Plan, which lowered qualification requirements so lower-income families could be eligible for the credit.
• EQUAL Act: Legislation to remove federal sentencing disparities between drug offenses – specifically crack cocaine vs. powder cocaine – failed to make the final cut. The bill, which passed the House in September 2021, would have established equal quantity thresholds – and criminal offenses/penalties – for both substances.
• SAFE Banking Act: The fair and safe Enforcement Banking Act, which the cannabis industry has been looking for a long time, also failed to make. It would have given cannabis businesses access to additional financial services, including digital transactions. The Senate did not vote on the legislation even though the House passed it on April 2021 for the fifth time.
• Big Tech regulation: a string of antitrust reform legislation was also not included in the spending package. The Open App Markets Act would impose additional regulations on app stores.
READ ALSO: $3,200 Payment To Residents Approved By Alaskan Lawmakers